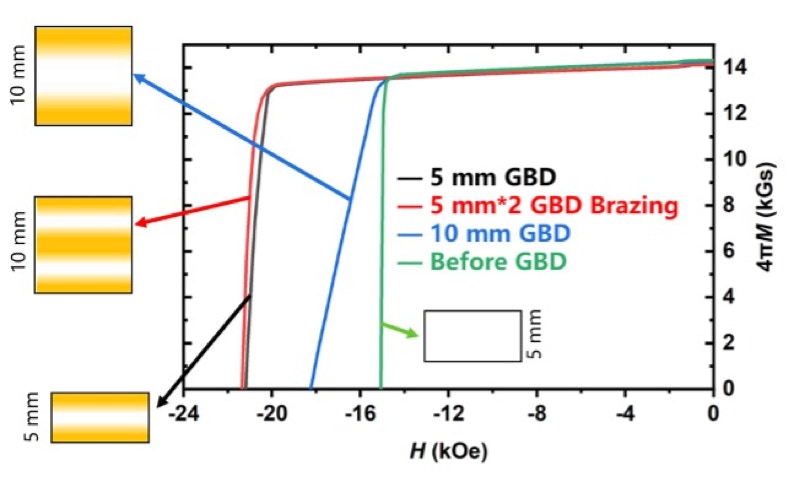
We introduce a GBD processing method that breaks the conventional thickness limitations of Nd-Fe-B magnets. This method enables the production of single-piece magnets with thicknesses previously unattainable, reaching up to 35 mm, while simultaneously enhancing key performance characteristics. Fig.1 shows the demagnetization curves of the 5mm GBD magnet, 10 mm GBD magnets and the 10 mm GBD-brazed magnet. The brazed magnet's magnetic properties are comparable to the 5mm GBD magnet's, with superior coercivity to the 10 mm GBD magnet. While increased magnet size can sometimes raise concerns about eddy current heating, our research demonstrates that this is effectively managed through careful selection of diffusant materials. Using this method, we have successfully fabricated large-block GBD magnets that were previously impossible, such as a 35 mm thick G52UH magnet.
That is not all.
While a high maximum energy product (BH)max indicates a strong magnet, simply using a strong magnet isn't always the most efficient solution. A Halbach array is a specific arrangement of permanent magnets that shapes the magnetic field, concentrating it strongly on the "working side" while significantly reducing it on the other. This is achieved by strategically orienting the magnetization direction of each magnet in the array.
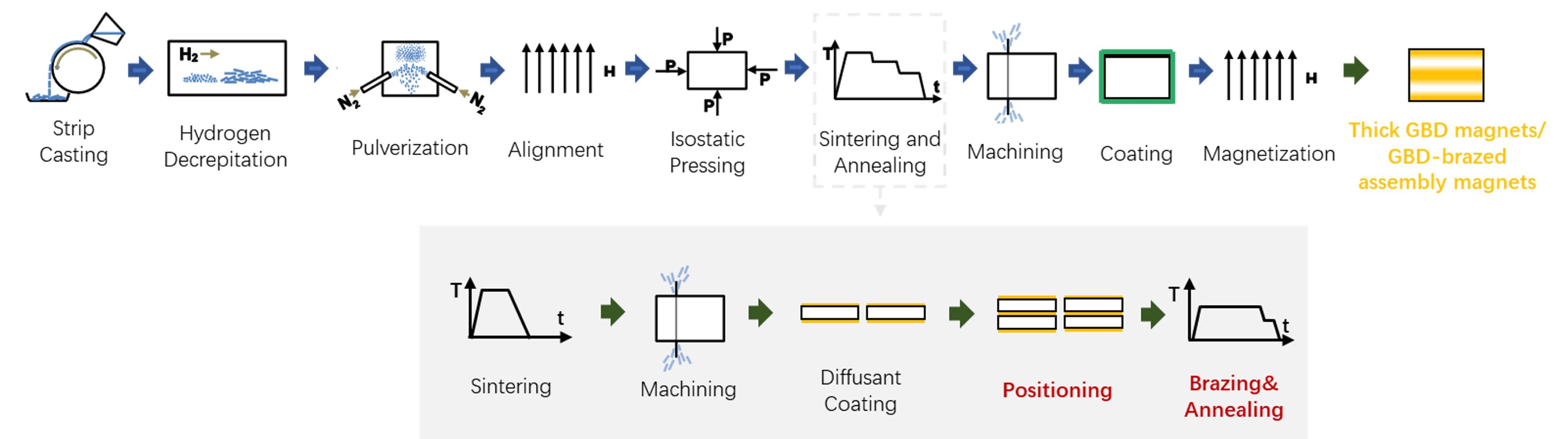
Critically, our process can be used to achieve this by the GBD-brazed assembly magnets meanwhile improving manufacturing by eliminating stacking and bonding after coating, significantly reducing assembly time and enhancing production scalability for high-volume applications. The GBD-brazed assembly magnet process, shown in Fig. 2, simply adds a positioning step to the typical GBD manufacturing process. This breakthrough not only preserves the intrinsic advantages of high (BH)max Nd-Fe-B magnets but also unlocks new design paradigms for compact, weight-sensitive systems, especially in the emerging lightweight, power-dense applications like consumer electronics, drones and humanoid robots.
For consumer electronics, such as pads, smartwatches and fitness trackers, GBD assembly magnets will allow for even slimmer, more comfortable designs that don't compromise on functionality. The increased efficiency will contribute to more sophisticated haptic feedback systems, providing users with richer and more nuanced tactile interactions. For drones, GBD-brazed assembly magnets will enable longer flight times, greater agility, and increased payload capacity. Similarly, humanoid robots require powerful, lightweight actuators with high torque-to-weight ratios for lifelike movement and extended battery life.
We provide comprehensive support for our customers' integration of this technology, bolstered by the protection afforded by our granted patents in China, the US, and the EU. If you are interested in this, do not hesitate to contact us.